ODOT has been awarded $33 million to construct a bridge for animals over one of the state’s most perilous sections of highway
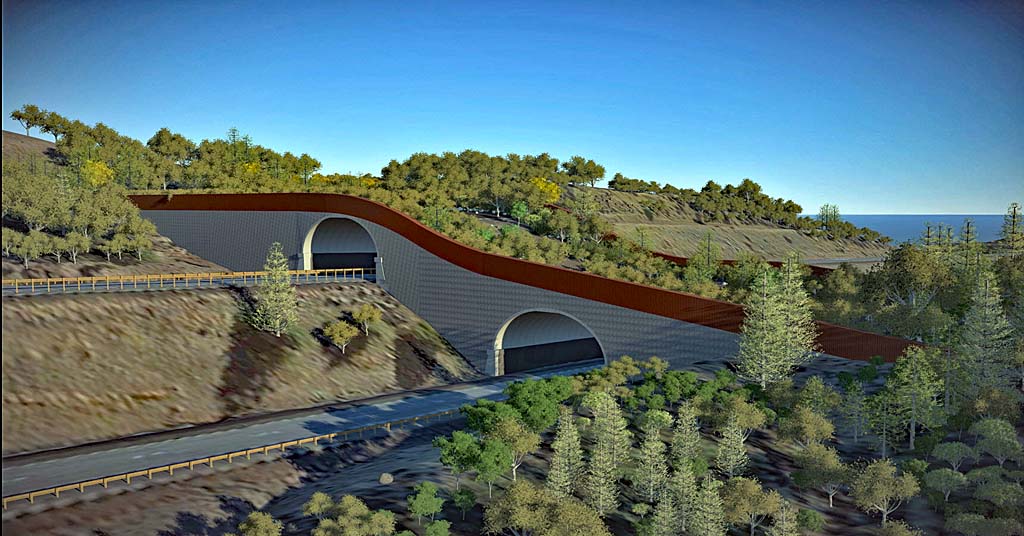

Movin’ on up: Artist’s rendering looking southeast at a proposed wildlife crossing over I-5 in southern Oregon. Several locations for the project are being considered under a feasibility study. Image: ODOT
By Kendra Chamberlain. January 8, 2025. The terrain south of Ashland, Ore., stretching to the California border sits at an incredible intersection of ecological systems.
Here, the ancient Siskiyou Mountains meet the volcanic Cascades, the high desert of the Great Basin, the Klamath Mountains and the oak woodlands of Northern California.
Dubbed an “ecological wonderland” and home to an impressive list of flora and fauna, the area was designated as the Cascade-Siskiyou National Monument in 2000.
Plowing through all that biodiversity is Interstate 5, which carries 17,000 vehicles per day. The four-lane interstate essentially severs the monument into two.
Animals don’t have an easy time getting from one side of the road to the other. Due to its location, however, the area is a hotbed of wildlife activity and considered a “red zone” for vehicle collisions.
“The traffic volume on most portions of I-5 would be considered to be a permanent barrier to wildlife movement,” Tim Greseth, executive director of the Oregon Wildlife Foundation, tells Columbia Insight. “The oddity with this particular location is it’s smack dab in the middle of the Cascade-Siskiyou National Monument, which was established primarily because of the biodiversity of the region.”
Now there’s good news, for wildlife and motorists alike.
The area will soon get a lot safer thanks to a $33 million federal grant to the Oregon Department of Transportation (ODOT) to construct a massive wildlife crossing over I-5 just north of the Oregon-California border.
“The grant award will allow ODOT to construct a wildlife crossing over Interstate 5 in southern Oregon in the Cascade-Siskiyou National Monument,” according to the ODOT website. “This will be the first wildlife overcrossing for Oregon and for the entire stretch of I-5 between Mexico and Canada.”
Announced in December, the grant award for the Southern Oregon Wildlife Overcrossing is the result of years of work and collaboration spearheaded by the Southern Oregon Wildlife Crossing Coalition, which formed in 2021 to push for animal crossings in the monument.
ODOT will provide another $3.8 million in matching funds that will come from a pot of money created by the 2021 Oregon Legislature to support wildlife crossings across the state.
Construction is expected to begin in 2028, according to ODOT.
Overcross vs. undercrosss
Each year in Oregon, officials document about 6,000 vehicle collisions with deer and elk.
Wildlife crossings are effective at reducing such collisions.
Oregon’s six existing wildlife undercrossings—tunnels constructed beneath roads—have resulted in an 80-90% decrease in vehicle-wildlife collisions in impacted areas, according to ODOT and the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife.
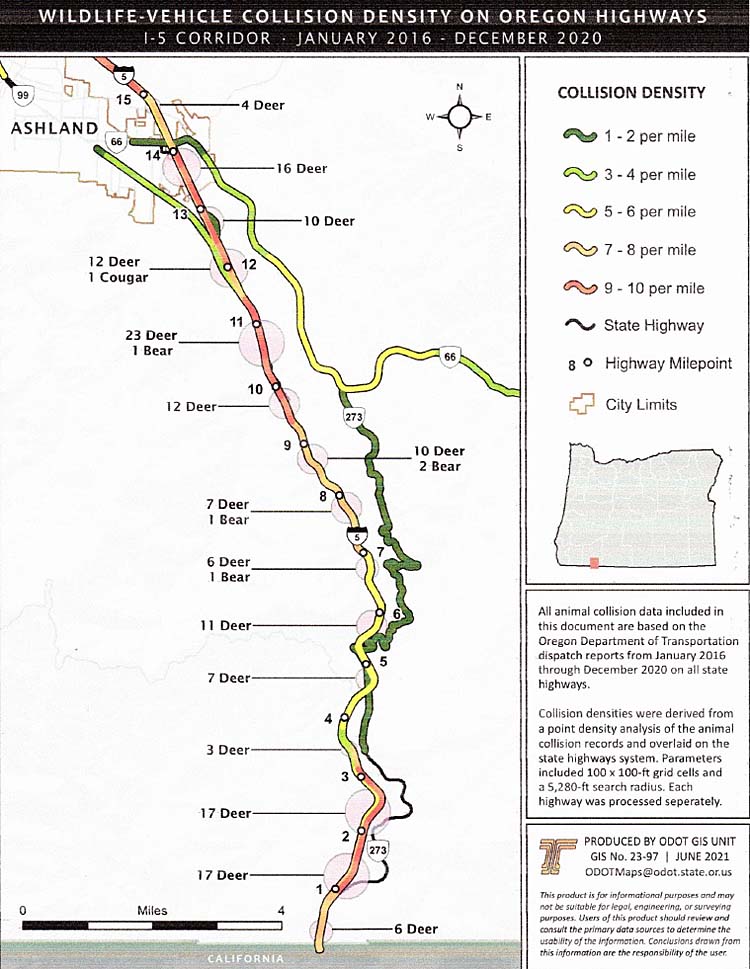
Vehicle collisions with wildlife on I-5 south of Ashland, Ore., between January 2016 and December 2020, included accidents involving 159 deer, five bears, one cougar and many unknown animals. The average cost of a deer collision in Oregon was $9,068. The average cost of collisions with elk was $24,006. Chart: ODOT/Southern Oregon Wildlife Crossing Coalition
“There’s a real advantage to doing overcrossings versus undercrossings,” says Greseth. “Overcrossings get a lot more diversity of species use. If you think about an underpass—and think about even people and how we might approach something where we’re going underneath a busy road—each of us individually would probably approach that with some trepidation. Animals aren’t going to be different.”
The proposed I-5 overcross will consist of soil, vegetation and landscaping elements to make the crossing feel safer to wildlife. It will include retaining walls and sound walls along its length to dampen interstate noise and shield wildlife from light on the road.
Dense plantings of vegetation will offer cover from predators for smaller animals, while open paths along the crossing will give animals using the bridge the ability to see their destination, according to ODOT spokesperson Julie Denney.
ODOT’s landscape architect and a multidisciplinary subgroup are planning which plants to use on the bridge. The team is “focusing on the plants that will help make the crossing the most attractive for the species we expect to utilize the crossing,” says Denney. Those species include deer, elk, bear, cougar, birds and even insects.
Potential plants for the crossing include sugar pine, desert gooseberry, deer brush, Oregon white oak, dwarf Oregon white oak, rubber rabbitbrush, antelope bitterbrush and spreading dogbane.
The structure will span northbound and southbound lanes, and have fencing stretching two-and-a-half miles in each direction and on either side of the interstate. The fencing will help funnel wildlife onto the bridge.
“Our goal is to provide an environment for the crossing to be as natural as possible, hopefully in a way that the wildlife are unaware they are crossing a major interstate,” says Denney.












Thanks for this article. Why will it take until 2028 to start construction? Will funding be sufficient four years from now?