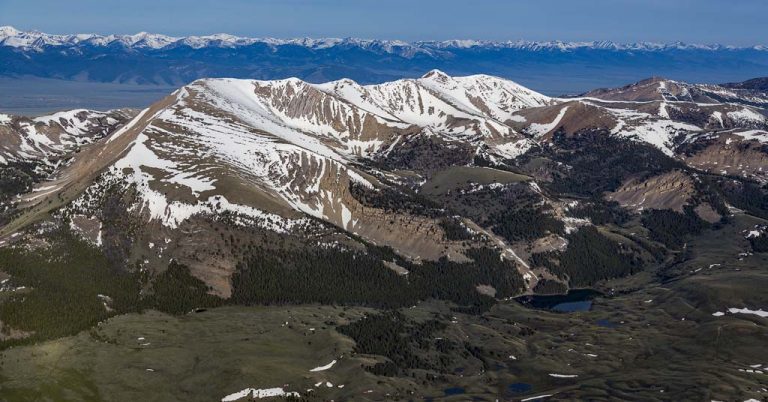
A growing number of scientists are investigating what they say is an overlooked threat to the world’s plants
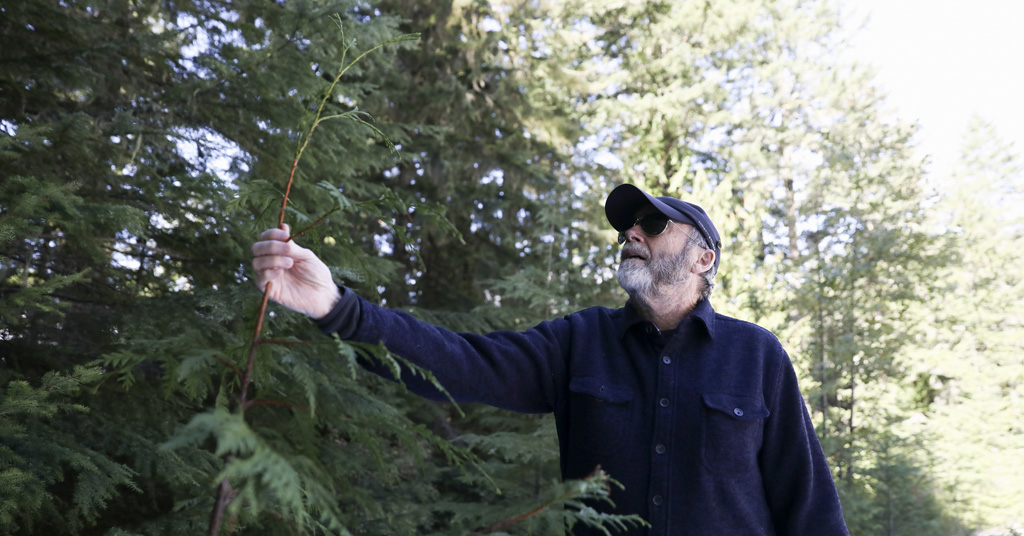

Peter Beedlow, a scientist at the Environmental Protection Agency, inspects a young western redcedar in the Willamette National Forest, Ore. A growing number of scientists are investigating what they say is an overlooked threat to the world’s plants—climate change-driven extreme heat. Photo: AP Photo/Amanda Loman
“Trees of the Pacific Northwest” is a climate journalism collaboration between Columbia Insight, The Associated Press and Global Climate Desk. Today, the second of three stories co-published by the collaborating newsrooms examines issues affecting trees of the Pacific Northwest due to changing climate. The final story in the series, to be published next week, will report on assisted migration of trees. The collaboration, developed over a six-month period, is part of The AP Global Climate Desk’s coverage of climate and will be distributed throughout the AP’s global network. Columbia Insight is proud to be part of this series and thanks our readers and donors for continuing to support local environmental journalism. —Editor
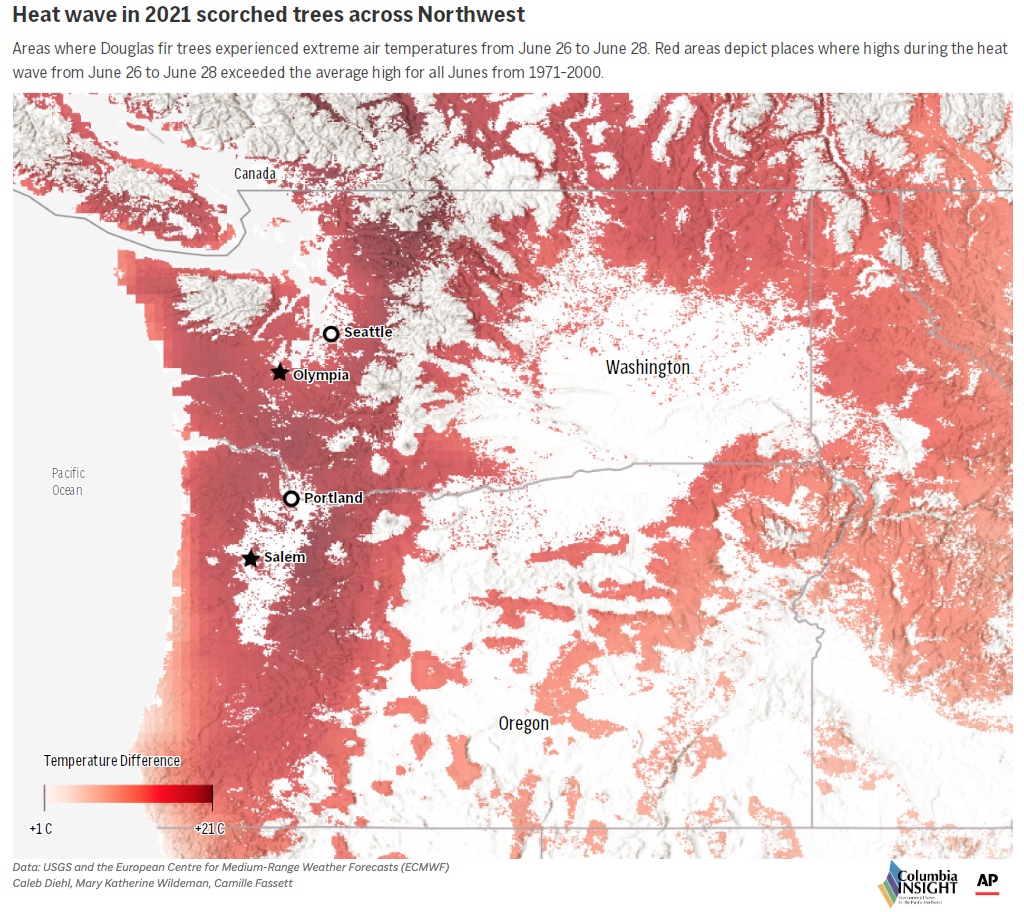
By Nathan Gilles. December 21, 2023. From June 25 to July 2, 2021, the Pacific Northwest experienced a record-breaking heat wave that sent the normally temperate region into Death Valley-like extremes that took a heavy toll on trees as well as people.
Seattle and Portland, Ore., recorded their hottest-ever temperatures, reaching 108 degrees Fahrenheit (42.2 Celsius) and 116 Fahrenheit (46.6 Celsius), respectively. In British Columbia, the small town of Lytton reached 121 degrees Fahrenheit (49.6 Celsius).
What become known as the “heat dome” is estimated to have killed hundreds of people in Oregon, Washington and British Columbia.
As this human tragedy unfolded, a lesser-known ecological tragedy was happening, one that scientists warn has grim repercussions for the world’s plants and the many animal species that depend on them.
In a matter of a few days, the 2021 heat dome turned many of the green leaves and needles on the region’s trees to orange, red and brown.
But, as recent research suggests, tree foliage didn’t simply dry out in the heat. Instead, it underwent “widespread scorching.”
“A lot this reddening and browning of leaves was just that the leaves cooked. It really wasn’t a drought story,” said Chris Still, professor at Oregon State University’s College of Forestry and a leading researcher on the effects of heat on trees.
Still is part of a growing number of scientists investigating what they say is a new, woefully underestimated threat to the world’s plants: climate change-driven extreme heat.
Sunburned forests
In recent years, scientists in the Pacific Northwest have linked the decline of 10 native tree species to drought.
In many cases, conditions that have brought about the decline are known as “hot droughts.”
Driven by above-normal temperatures, hot droughts can be far more damaging to trees than droughts that result simply from a lack of moisture.
Hot droughts not only dry out soil; they also dry out the air. This stresses trees, and can cause water-carrying tissues inside them to collapse—a process called “hydraulic failure.”
In a paper earlier this year in the journal Tree Physiology, Still made the case that damage to the region’s trees during the heat dome was triggered primarily by direct damage from heat and solar radiation rather than indirectly by drought caused by the extreme heat.
“I’m not trying to say that drought is not a huge and important factor,” said Still. “But I think with events like the 2021 heat wave becoming more common and intense, it’s important to look at the response of trees and other plants to these events and not just at drought, which has been the dominant paradigm.”
Still’s argument includes the observation that “foliage scorch” was primarily found on the southern and western sides of trees and forests—a pattern that follows the track of the sun across the summer sky.
“Basically, it was like a sunburn across the entire forest. It was quite disturbing,” said co-author Daniel DePinte, U.S. Forest Service aerial survey program manager, who observed the phenomenon from an airplane.
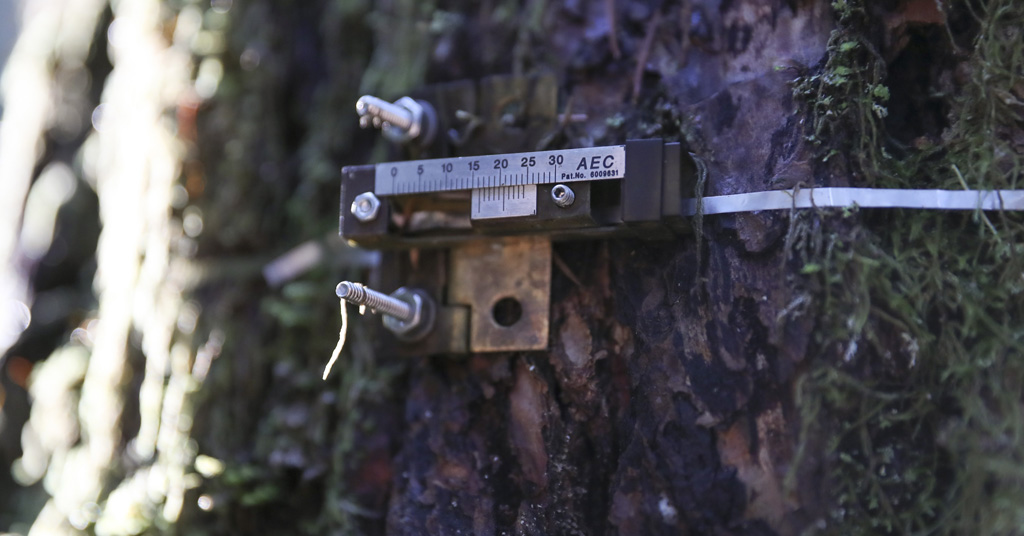

A dendrometer, a device to measure tree growth, on a Douglas fir in the Willamette National Forest, Ore. Photo: AP Photo/Amanda Loman
Multiple tree species were scorched, DePinte said, noting that the role played by the sun became clear when the same trees were viewed from an orientation not exposed to direct sunlight.
“It almost appeared as if the forest damage disappeared,” he said.
The paper was written in response to an earlier study published in the same journal that argued a different position: that the heat dome led to wide-spread drought stress and hydraulic failure in Pacific Northwest trees.
“Overall I agree … that heat damage played a big role in the damage caused to trees (during) the 2021 PNW heat wave. But in my view, hydraulic failure was as important, if not more,” wrote that study’s lead author Tamir Klein, professor of plant and environmental sciences at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel.
Heat limit
Exactly how hot is too hot for trees and other plants is the research focus of William Hammond, a plant ecophysiologist at the University of Florida.
Hammond called the scientific community’s current understanding of extreme heat’s effect on plants a worrying “blind spot.”
“One thing is for sure, we know a lot more about how dry is too dry for plant survival than we know about how hot is too hot,” he said.
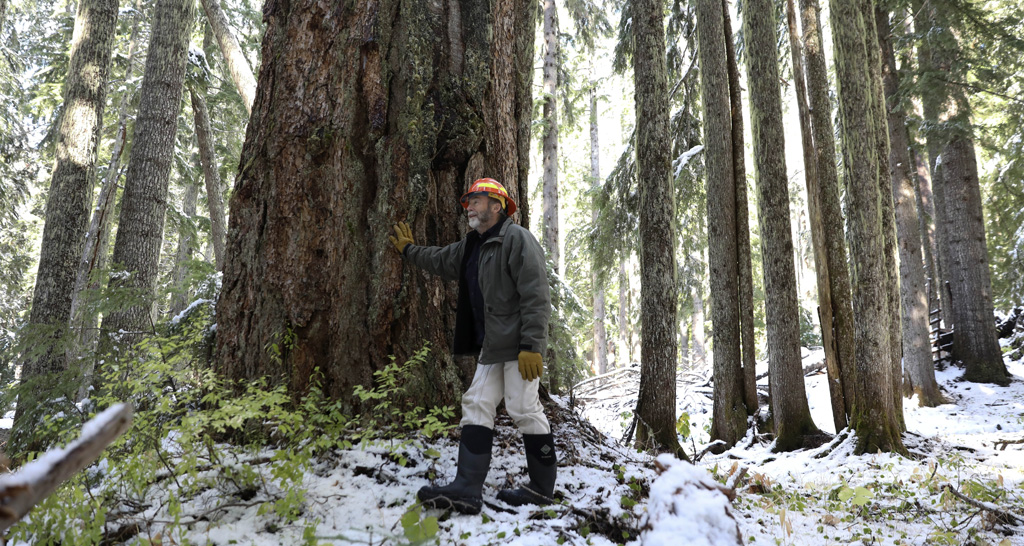

EPA scientist Peter Beedlow among old-growth Noble fir trees in the Willamette National Forest, Ore. Photo: AP Photo/Amanda Loman
What scientists call “thermal tolerances” have been established for just 1,028, or less than 1%, of the world’s 330,200 recognized land-based plants, according to a frequently cited 2020 paper in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
No single thermal limit fits all plant species, but in general extreme damage to plant tissues occurs around 122 degrees Fahrenheit (50 Celsius), Hammond said.
“With those temperatures you might think ‘wow, the air doesn’t get that hot,’ but that’s the temperature of the plant, not the temperature of the air. And those things can be quite different,” he said.
Just how different is something Still has been tracking.
During the heat dome, he and colleagues recorded air temperatures around a Douglas fir tree reaching 112 degrees Fahrenheit (about 44 Celsius), the hottest ever recorded in the forest where the measurements were taken. The needles of the tree, however, reached 124 Fahrenheit (51.1 Celsius) due to exposure to direct sunlight.

Mushrooms on a fallen Noble fir tree in the Willamette National Forest, Ore. Photo: AP Photo/Amanda Loman
Still says observations like this and similar ones in forests around the world dispute a common misconception even among some scientists that plants can withstand extreme temperatures and stay cooler than air around them, especially when given access to water.
“Plants can control their temperature to some degree, but if the heat is extreme enough, some plants won’t be able to get through it even if they have a ton of water,” he said.
Hammond has reached the same conclusion based on work in his lab.
“If temperature gets high enough, heat stress can kill living plant tissues even if they have water,” said Hammond.

 Columbia Insight’s reporting on biodiversity in the Columbia River Gorge is supported by the Autzen Foundation and Pacific Power Foundation.
Columbia Insight’s reporting on biodiversity in the Columbia River Gorge is supported by the Autzen Foundation and Pacific Power Foundation. 








