Young cougars that lose their mother typically starve to death. Wildlife officials are seeing more of them
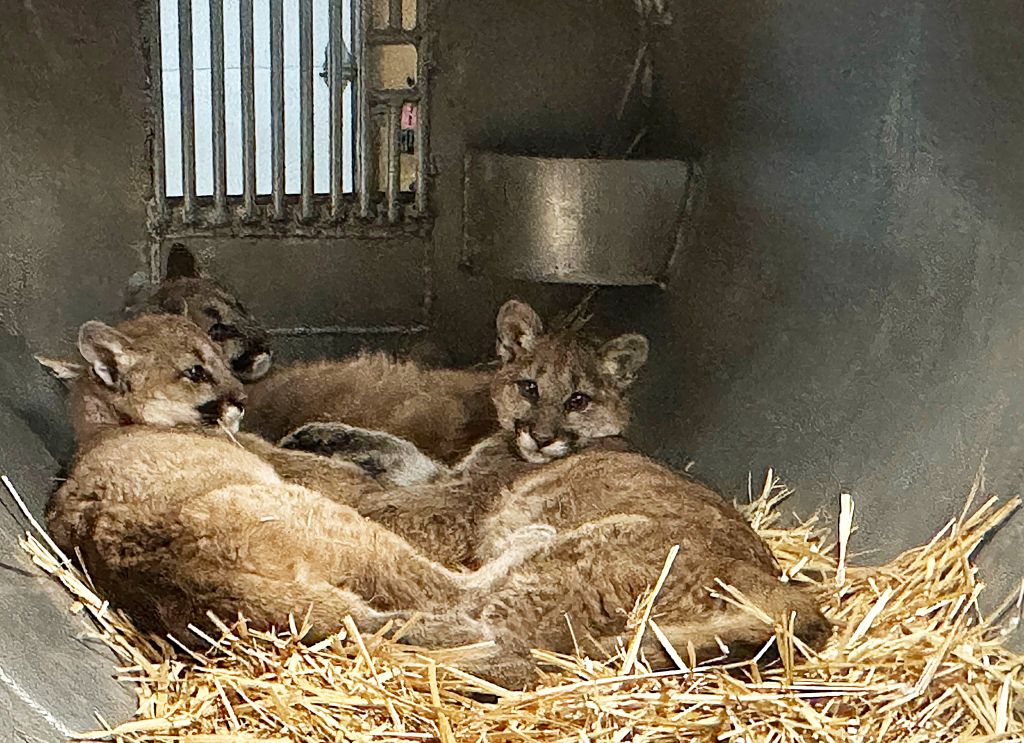

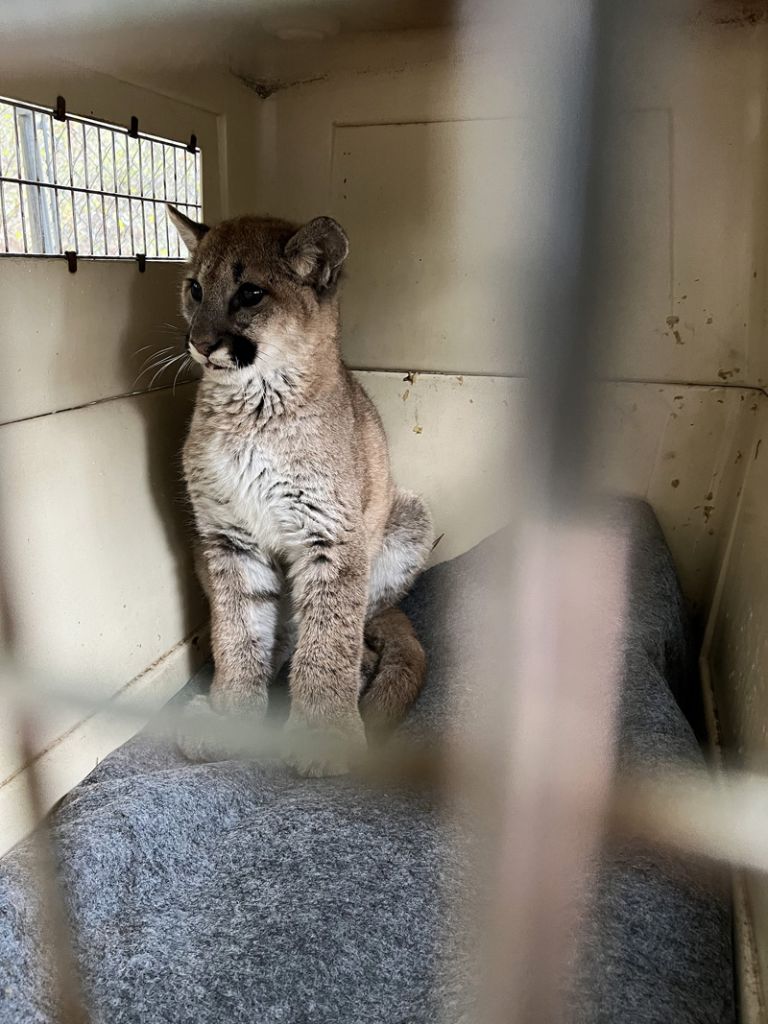
Captured in Klickitat County, Wash., earlier this month, these orphaned cougar siblings await transport to new homes. Photo: WDFW
By Dawn Stover. November 28, 2023. About six months after she and her family moved into an off-the-grid house on 35 acres near Husum, Wash., Kelsha Erickson started losing chickens.
In October, she lost four birds in less than two weeks.
That put an end to free-ranging for the three remaining chickens. Erickson confined them to a pen she built from fence panels and chicken wire.
“I had accepted the risk to my chickens, and knew I didn’t have a completely secure structure, because having toddlers, there are limitations to what you can get done in a day,” she says. “I thought we were good.”
But on Nov. 14, while she was in town, her husband called to tell her that bobcats or cougars had killed another chicken.
One of the cats had reached into the pen and decapitated a chicken but was unable to pull its body through the fence.
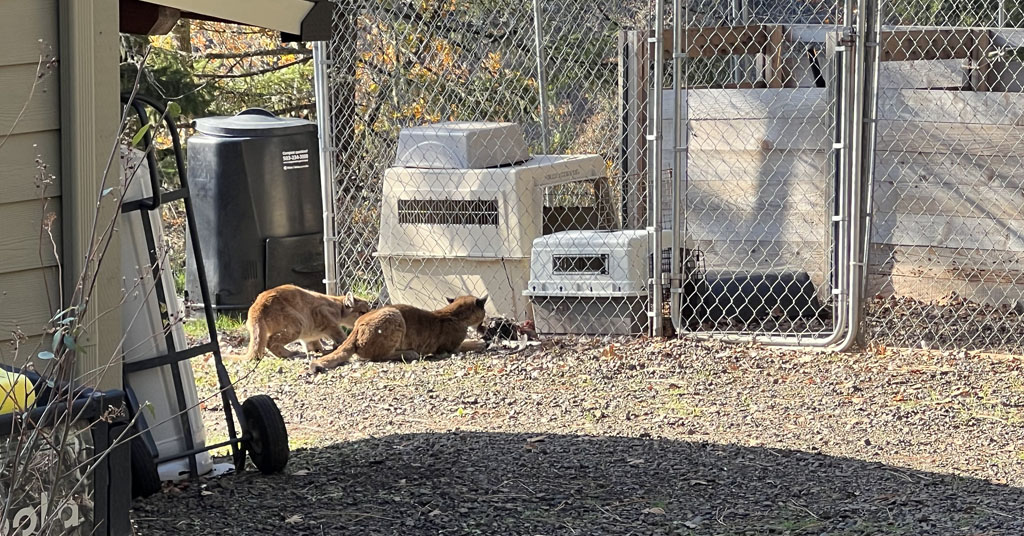

Cougar kittens contemplate a chicken dinner at a private residence in southwest Washington. Photo: Abram and Kelsha Erickson
The culprits turned out to be three very hungry cougar kittens that lost their mother before they learned how to hunt wild prey.
Without her, they wouldn’t survive the winter.
But Erickson and wildlife specialists at the Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife intervened.
Starving orphans
When Erickson got home from town, she found two frustrated cats outside her chicken pen.
She fired a few shotgun shells to scare them off.
Ten minutes later, she heard her dog growling. The cats were back, desperate for a chicken dinner.
Erickson emailed a photo of the cats to a neighbor, who told her they were cougar kittens that looked emaciated.
The next morning, Erickson called the Washington Fish and Wildlife Department’s local wildlife conflict specialist, Todd Jacobsen, to tell him about the three kittens. She’d already consulted him earlier when she thought she was losing chickens to a bobcat.
“Within four hours, he was up here,” says Erickson.
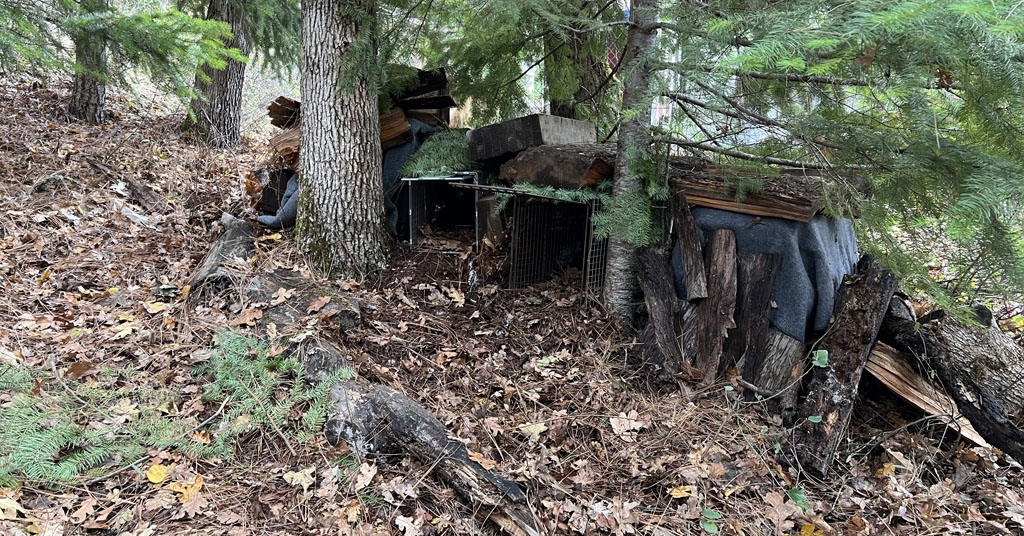

The trap and camouflage constructed to capture three cougar kittens in southwest Washington. Photo: Abram and Kelsha Erickson
Jacobsen set up trail cameras to look for an adult accompanying the kittens but didn’t see one.
“The fact that [the kittens] were out by themselves and showing up during the day at the same residence, that’s not normal cougar family behavior,” he says. “I am certain that they were orphaned.”
It’s not clear how the mother died.
Cougar mothers “don’t just walk away or abandon their young,” says Richard Beausoleil, the state wildlife agency’s cougar and bear specialist. “Something happened.”
Four cougars were killed within the same game management unit as the Ericksons’ home during the month before the kittens were discovered, but there’s no evidence that one of them was the kittens’ mother.
Jacobsen offered Erickson options for dealing with the kittens.
She chose to help him trap the kittens so that one of his colleagues could try to find a new home for them.
Cougar country
A year ago, Erickson and her husband and their twins—a boy and a girl who will be two years old in December—were living in Lake Oswego, Ore., a Portland suburb. Erickson saw a real estate listing for a remote, ridge-top property on a logging road in Washington’s Klickitat County and showed it to her husband.
At first it was a joke, but by May 2023 they’d bought the house and moved in.
Erickson spent her early childhood in Alaska and is no stranger to rural living. Still, she wasn’t expecting to see so many rattlesnakes near her new home.
With two toddlers, she worries more about the snakes than cougars.
“Seeing cougars at all is a pretty rare occurrence, and it’s even more rare to see cougar kittens,” says Jacobsen.
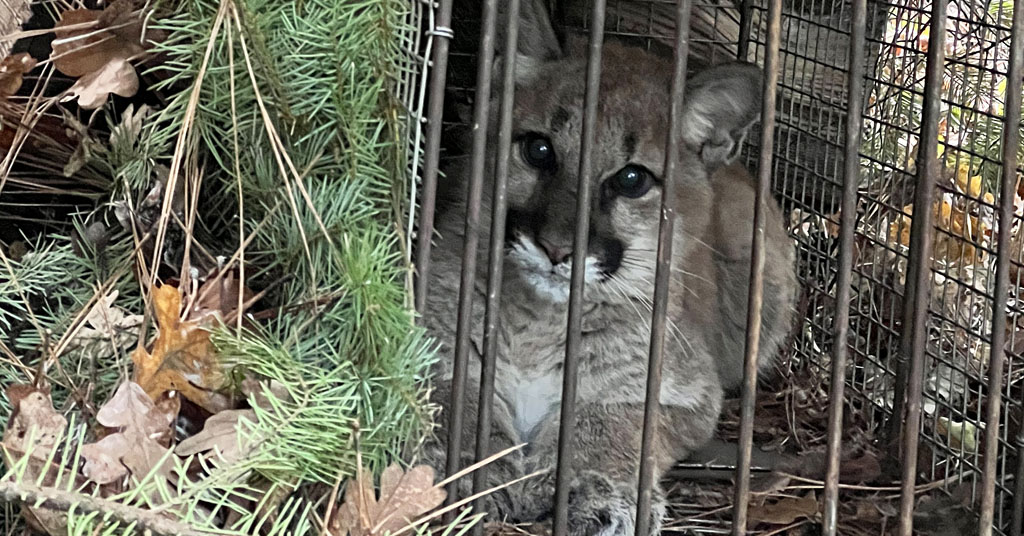

Without mothers to teach them hunting and survival skills, cougar kittens usually die of starvation. Photo: Abram and Kelsha Erickson
At Erickson’s house, Jacobsen set up live traps as well as cameras. He hung meat in the traps.
By morning, two of the kittens were caught.
Jacobsen and a co-worker transferred the two captured animals to kennels.
The kennels had livestock dishes with food for the cats. Erickson used a funnel to give them water.
The next morning, they found the third kitten in a trap and transferred it to a kennel.
Jacobsen and his colleagues fed the animals again then transported the kennels to Beausoleil in Wenatchee, Wash.
Before they left, Erickson took some photos.
“If you weren’t there hearing them with this low growl and swatting at the door, they do look rather cuddly,” says Erickson. “But they’re not cuddly, not if you want to keep your fingers and your eyes.”
“We’ve been calling them ‘spicy’ kittens,” she says.
Killing of female cougars on the rise
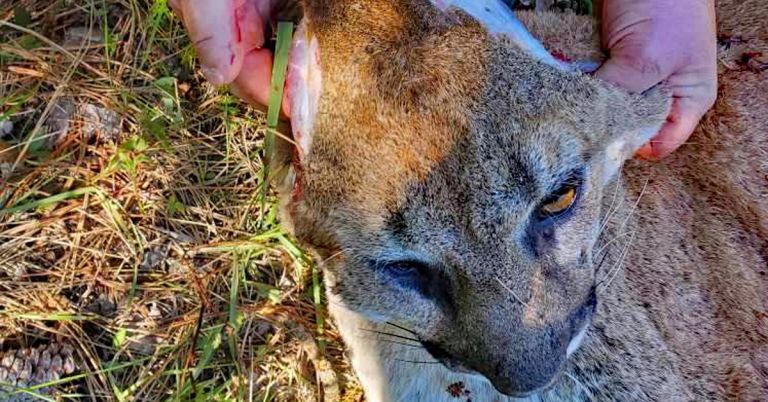
When the kittens reached Beausoleil he chemically immobilized them, examined them and used tweezers to remove a birdshot pellet from one of the kittens. The shot had come from Erickson’s warning blast, but the injury was superficial.
Beausoleil reported that the kittens were thin but doing okay.
The three animals, two males and one female, all weighed between 21 and 23 pounds.
Beausoleil estimated their age at approximately 17 weeks, based on their size and eye coloration. Cougar eyes change from blue to yellow as the animals mature, and cougars typically stay with their mothers until they’re about 18 months old.
Klickitat County (red) borders the Columbia River. Map: Wikimedia Commons
Two facilities accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums have agreed to take the orphans. Two of the kittens will go to North Carolina, and the third to Pennsylvania.
They are scheduled to be transferred by plane today.
Washington cougar kittens that have been placed at zoos over the last 20 years have been seen by about 40 to 50 million people, Beausoleil says. “There’s a lot of nationwide education in that.”
In southwest Washington’s Region 5—which includes Klickitat, Skamania, Clark, Cowlitz, Wahkiakum and Lewis Counties—this is the third litter in 13 months that Jacobsen’s team has rescued.
During his six previous years on the job, there were none.
The first capture happened in October 2022, in the town of Klickitat. A domestic dog had killed one kitten, but its two littermates were rescued and sent to the Houston Zoo.
A second litter was captured in May 2023 after a landowner shot a female cougar while it was killing a sheep near Kalama. One of the kittens died, but two others survived and ended up at the Philadelphia Zoo.
While these kittens will spend their lives in confinement, young cougar kittens typically starve to death when they lose their mothers to hunting, vehicle collisions, disease or other causes.
Even at seven or eight months, cougars may not be able to survive on their own, says Beausoleil.
Cougar advocates who have studied mortalities in Washington are concerned that hunters may be killing too many females, particularly in the area where two of the recent kitten rescues occurred.
In five of the six past years, 62-73% of hunter harvests reported in the two population management units (PMUs) located in Klickitat County and eastern Skamania County have been female.
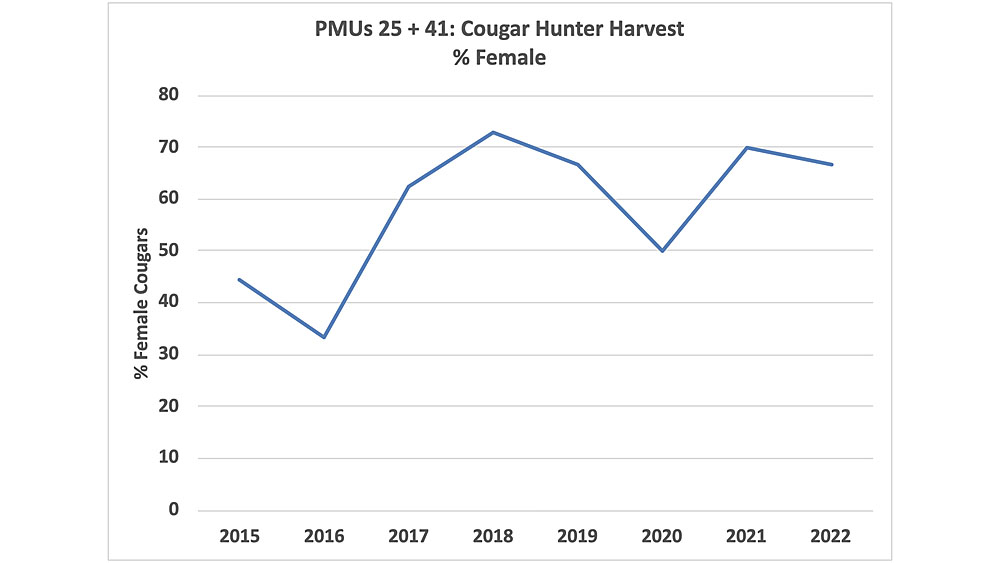
In recent years, the majority of cougars killed by hunters in population management units (PMUs) covering Klickitat County and eastern Skamania County have been female. Data source: WDFW cougar harvest statistics
The Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife is assessing the latest cougar population information statewide.
The findings will be reported in the Game Management Plan currently being updated and scheduled for release in draft form next summer.
“Locally, there’s no doubt the mortality is higher than we want it,” says Beausoleil.
The continuing removal of cougars by the Klickitat County Sheriff’s Office has contributed to the rise in mortalities in the county.
Cougar spotting
In Washington, it’s unlawful to kill spotted kittens (which usually weigh less than 80 pounds) or adult cougars accompanied by spotted kittens.
However, Jacobsen says “it can be really challenging” for people to tell male and female cougars apart—or even to correctly identify a cougar.
The majority of “cougar” sightings reported to the wildlife agency turn out to be house cats.
Adult females are typically smaller than males, and nursing females tend to have darker fur around their teats, but this marker is difficult to see.
Males have a black penis sheath—a black spot about the size of a quarter located between the legs and a few inches below the anus—that is also difficult to see, because it’s usually covered by the tail when the cougar is moving.
Jacobsen encourages anyone who sees a cougar to call the Fish and Wildlife Department hotline: 877-933-9847.

Captured in November, this cougar kitten will likely never again see its Pacific Northwest forest home. Photo: Abram and Kelsha Erickson
“Seeing cougar kittens by themselves on multiple days is a pretty good indicator that they’re orphans,” he says.
Jacobsen also encourages hunters to spend time observing a cougar before shooting. That may enable the hunter to determine whether the cougar is a mother with kittens.
Erickson grew up in a family of hunters and says she wouldn’t be opposed to shooting an adult cougar that’s a persistent threat.
But she’s glad she got the chance to help state wildlife experts “find a better solution for the kittens than starvation or getting killed by hunters.”
She’d like other people experiencing cougar conflicts to know that there are nonlethal alternatives available.












Stop the killing! These animals ought to be left alone to care for their young and be an integral part of their ecosystem. Zoos do not educate: They put animals in brutally unnatural displays so they can profit off of them.
Thank you, Dawn Stover! Only the Fish and Wildlife Commission can reduce the killing of female cougars with kittens, and now is the time to tell them. WDFW’s cougar and bear hunting rules and seasons were liberalized since 2017, and WDFW’s posted data shows that cougars have been overhunted well above sustainable levels for seven years straight. Research in WA and other states show that cougars do not overpopulate, because they compete for territory, and that hunting is not needed to control their numbers. Studies show that overhunting of cougars disrupts their social structure, leading to increased conflict with humans and domestic animals, as seen in this article. The number of bears killed by hunters in WA also has doubled in the past five years. WDFW now has data showing that the population of bears in WA is considerably lower than they had thought. At the Dec 14-16, 2023 meeting of the WA Fish & Wildlife Commission, the Commission will consider a petition asking WDFW to reduce cougar and bear hunting back to sustainable levels. Please write to commission@dfw.wa.gov and ask Commissioners to vote FOR the petition to reduce cougar and bear mortalities to scientifically-determined sustainable levels. Scientists have shown that killing too many does harm to these species, and harms the ecosystems that greatly rely on what these apex carnivores do.
As always, Dawn Stover writes well-researched articles on environmental issues. The statement “The findings will be reported in the Game Management Plan currently being updated and scheduled for release in draft form next summer,” however, is the agency’s stated propaganda, but the GMP is already three-years past due, and in the interim years, WDFW removed the expiration dates on its cougar and bear hunting rules, so as to not have to update them. It also ignored its science and increased killing quotas. The petition mentioned by Star in an earlier comment is to set the quotas on bears and cougars back to about 2019 levels when there was at least a nod to science. The agency had set those earlier quotas to (basically) the maximum population replacement rate if there were no hunting, but without any safety margin for disease, fires, drought, extreme weather, loss of habitat and connectivity, etc. The current allowances are well-above the ability of the bears and cougars to replace their death losses. Please write the commission as Star requests.
Columbia Insight welcomes comment and opinion on all stories posted on our website and social media platforms, including those that respectfully disagree or take issue with the facts or points of view presented in stories. We reserve the right to delete any comments that include profanity; are intended to induce rancor; are dishonest; or insult other members of our community. Comments on this story or posted as part of this thread have been removed because they do not align with these standards.
The Fish and Wildlife hotline mentioned at the end of the article– is this for Washington residents only, or does this also work for Oregon?
Why not euthanize? Can’t feed people but someone will feed them??? Why aren’t deer protected????
Please. I do not believe the stories that there’s plenty of them. Threat to flowers?